High-Temperature Fuel Cells for Mobile and Stationary Applications
Application of SOFCs In Combined Heat, Cooling and Power Systems
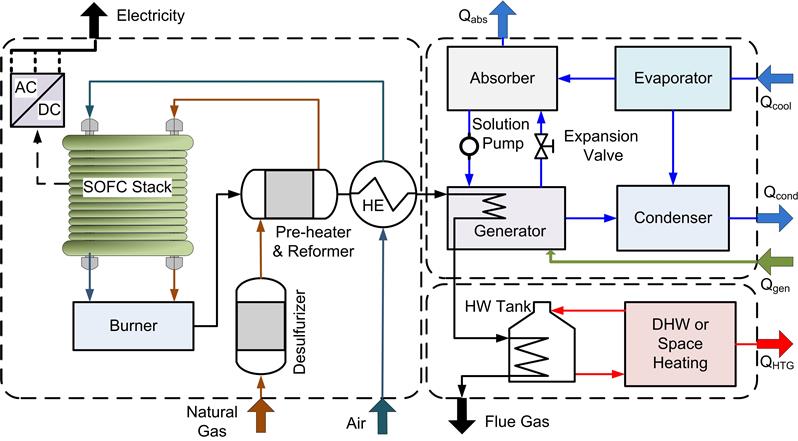
The unique characteristics of solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) have encouraged their development for a wide variety of applications that range from portable, mobile and micro-combined heat and power (500W to 20 kW) to larger-scale stationary power at both distributed generation (100kW –5MW) and central utility scales (100 MW). Attractive SOFC technology attributes include high electric efficiency, high-grade waste heat, fuel flexibility, low emissions, power scalability, and low unit capital cost potential when high production volumes are achieved. The high operating temperature of SOFCs enable production of varying grades of waste heat that can then be recovered for process heating, power augmentation via gas turbine integration, or for polygeneration of exportable products (e.g., heat, cooling, power or fuels). The effective use of waste heat significantly impacts overall system efficiency, economics and environmental emissions. These attributes have accelerated SOFC technology development with the aim of replacing traditional combustion-based power generation equipment, as well as offering solutions to emerging 21st century energy problems.
This work focused on synthesizing advancements in SOFC systems technologies towards deployment in commercial building applications.
PUBLICATIONS
- R.J. Braun and P. Kazempoor, “Application of SOFCs in Combined Heating, Cooling and Power Systems”, Chap. 12, in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: From Materials to System Modeling, T.S. Zhao and M. Ni, editors, Energy and Environment Series No. 7, Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, U.K. (2013), 56 pages.
Current Projects
Past Projects
Selected Publications in This Research Area
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
View Other Research Areas:
MODELING AND SYSTEMS ANALYSIS OF ALTERNATIVE FUEL PRODUCTION AND UTILIZATION SYSTEMS
RENEWABLES AND GRID-ENERGY STORAGE SYSTEMS
